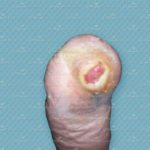
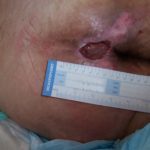
Interactive Wound Dressings
Wound dressings are sometimes described as passive, active, or interactive. While passive wound dressings simply serve a protective function, active dressings actually promote healing through the creation of a moist wound environment. Interactive wound dressings, on the other hand, not only create a moist wound environment but also interact with the wound bed components to…