Wound Bed Preparation – TIME Mnemonic
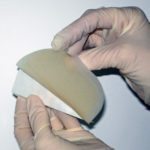
As we have seen, the TIME mnemonic can be used to capture the fundamental principles of wound bed preparation.1,2 Become a professional at appropriate dressing selection for the different stages of wound healing within the TIME trick. As no single wound dressing is suitable for all wound types or healing stages, wounds should be assessed…