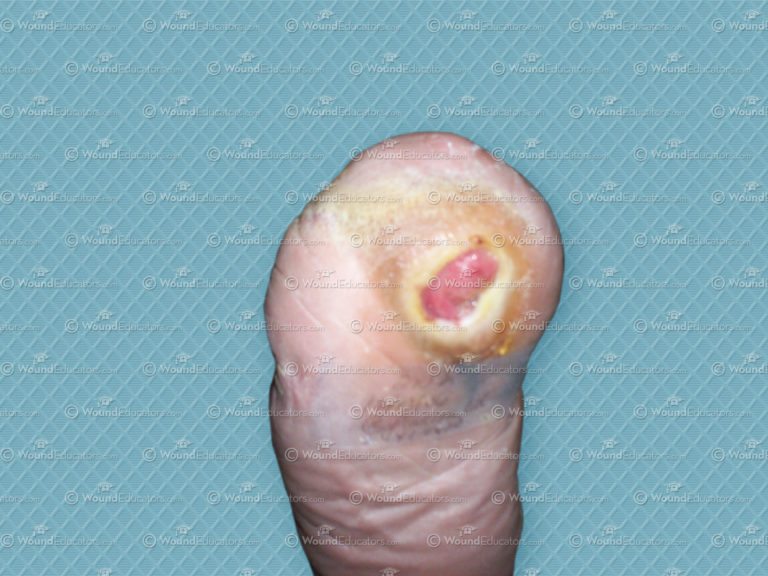
The Resurgence of Honey in Wound Management
Although honey has been used in wound management for centuries, and is mentioned in the Koran as a medicine for all disease, its popularity declined with the increasing availability of modern antibiotics, antiseptics and improved surgical techniques. However, with the continuing battle against wound infection and interest in the antimicrobial properties – honey in wound…