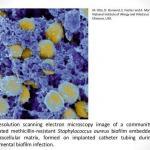
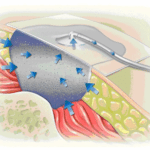
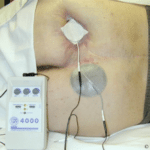
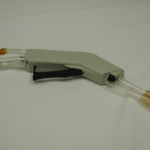
Advanced Modalities – Free Wound Care Resources
Chronic wounds and wounds that fail to progress through the phases of wound healing as expected, may require additional interventions to enhance wound healing. There is significant research and consensus on the use of most standard interventions such as saline irrigation, whirlpool, and the previously- described concept of moist wound healing, However, there is less…