Wound Care Education: How Do Wounds Affect YOUR Skin?
The process of wound healing is a complex bodily function. This natural process involves inflammatory vascular and connective tissue working in tandem with epithelial cells over a period of time. As such, wound care education requires a basic understanding of how wounds actually affect the connective tissue that is human skin.
Our skin consists of cells, fibers, and an extracurricular matrix that combine to form the following four layers:
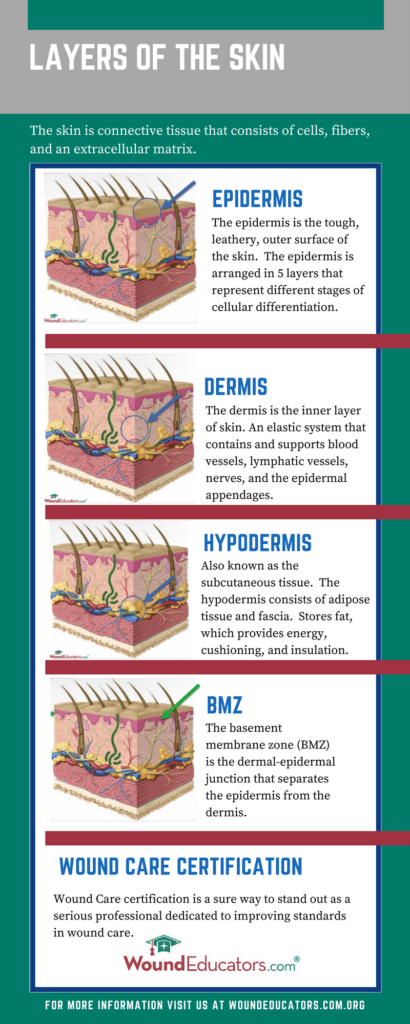 The first layer is called the epidermis. This is the outermost layer of skin and is visible to the naked eye. This first layer is itself composed of five layers, each representing a different stage of cellular differentiation, and functions as a basic layer of protection against environmental factors and threats.
The first layer is called the epidermis. This is the outermost layer of skin and is visible to the naked eye. This first layer is itself composed of five layers, each representing a different stage of cellular differentiation, and functions as a basic layer of protection against environmental factors and threats.- The inner layer of living tissue just below the epidermis is called the dermis. The dermis is an elastic system supporting blood and lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, and epidermal appendages (e.g. sweat glands, hair follicles).
- In between the epidermis and dermis is a dermal-epidermal seam known as the basement membrane zone (BMZ). The BMZ is not only a critical interface that separates the epidermis from the dermis, but is also a highly specialized structure that allows for communication between different cell types.
- Below the dermis is the last layer of skin known as the hypodermis, or subcutaneous tissue, and it is composed of fascia and adipose tissue. The hypodermis serves to fasten the skin to the underlying surface, and it should be noted that the rest of the body’s tissues and organs reside right beneath the hypodermis. The hypodermis is also important because it stores fat. The body uses fat for thermal insulation, as an energy source, and for cushioning (i.e. absorbs shocks from impacts to the skin).
Now that you have a basic understanding of the skin and how its four layers function, we can move on to basic wound care education. Before knowing how to dress a wound, you must first analyze the wound. As there are four layers to the skin, there are also four questions to keep in mind when determining the severity of a wound:
- How thick is the wound? A superficial wound involves only the epidermis and the upper dermis, whereas partial thickness reaches to the lower dermis, and full thickness goes all the way through to the subcutaneous tissue. Deep and complicated refers to penetration through the subcutaneous tissue and into natural cavities (i.e. organs, tissues, etc.).
- How complex is the wound? Simple means the wound affects only one organ or tissue, whereas combined means its affecting multiple.
- How old is the wound? A fresh wound occurred less than 8 hours prior, while an old wound means the injury occurred more than 8 hours ago.
- What is the origin of the wound? Here is a helpful list of some of the more common wound origins:
- Superficial – scratching, rubbing, picking, etc.
- Incised – usually due to surgical interventions
- Crush – made from a heavy blow delivered with a cutting tool (e.g. hatchet, sword)
- Lacerated – a sharp-edged object results in fragments of tissue being torn away
- Stab – pointed tool or weapon
- Contused – injury to tissue under the skin’s surface; most commonly a result of traffic accidents.
- Secondary – primary diseases (e.g. diabetic ulcers, pressure ulcers, venous ulcers)
- Other – other common wound origins can include bullet wounds, bite wounds, and poisoned wounds.
Wound healing is a complex process that involves three overlapping phases: inflammation, proliferation, and maturation. Wounds heal faster the more quickly they are attended to after the injury. When attending to a wound, the goal should be to keep it free from infection (ideally by dressing or closing it using appropriate methods) and to create an environment that promotes healing. To learn more about wound care education, check out our available wound care education courses or view our free wound care resources.
