Evidence-Based Wound Management
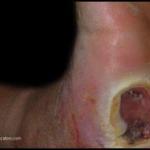
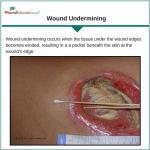
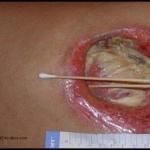
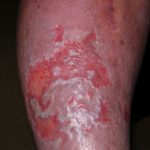
In an effort to improve and standardize patient care outcomes, evidence-based wound management has gained significant importance. By using evidence-based wound management when treating wounds, answers to common problems can be addressed resulting in improved patient outcomes. What is Evidence-Based Wound Management? Evidence-based medicine has been defined as the “conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of…